
Madrid, Community of
The Community of Madrid (CM) is characterized by a long agricultural tradition, although it has a very limited impact on the regional economy, while occupying one of the leading positions among food markets and consumer centers in the EU.
This reality means that its agri-food innovation system (AKIS) is particularly dispersed, and sometimes there are public and private agents that share other economic or knowledge areas.
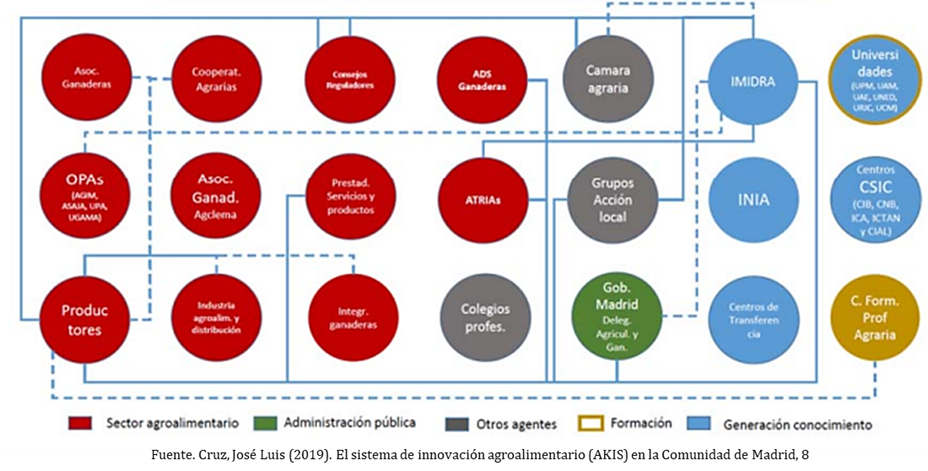
The image shows the groups of public and private agents in a regional AKIS and their relationships:
- Agents that generate knowledge.
- Agents of the Public Administration.
- Agents dedicated to training.
- Agents of the agri-food sector.
- Other AKIS agents.
AKIS agents and interactions
Agents dedicated to the generation of knowledge
- Universities: The Madrid region has the largest university and research population in Spain and one of the largest in Europe. Those centers with studies most directly related to the agroindustrial sector include the Rey Juan Carlos University , the Autonomous University of Madrid , the Complutense University of Madrid , the University of Alcalá , the UNED ( National University of Madrid), the UPM (which includes the ETSI Agronómica, Alimentaria y Biosistemas), and the CSIC (Spanish National Research Council).
- Madrid Institute for Rural, Agricultural, and Food Research and Development ( IMIDRA ). This is an autonomous body attached to the Ministry of Environment, Agriculture, and the Interior. It conducts R&D and other technological and promotional activities to support the development of agriculture, associated industry, and rural sectors linked to the natural environment.
- CM transfer centers related to the agri-food sector. The most closely related transfer centers are the OTRI of the INIA (National Institute of Technology), the Autonomous University of Madrid, the Complutense University, the University of Alcalá de Henares, the UNED (National University of Madrid), and the Polytechnic University of Madrid. In addition to these, the OTT of the CSIC (Center for Innovation and Technology Transfer) and the Center for Innovation and Technology Transfer (CINTTEC) of the Rey Juan Carlos University are considered of particular interest.
- Spanish National Research Council ( CSIC ) . The CM has 45 centers, although only a few of them are related to agriculture.
Public sector agents
- Ministry of the Environment, Agriculture, and the Interior : Department of the regional government responsible for agriculture and the agri-food industry, as well as rural development. IMIDRA is part of its structure.
- Agriculture and Livestock Delegations : These are 10 offices spread throughout the region. These are structures dependent on the regional government and deserve special mention for their dedication to providing specialized advice and information to the population.
Agents dedicated to training
- Vocational training. Of note are the Escuela de la Vid High School, which offers a curriculum for Agricultural Production Technician, and the Villaviciosa de Odón Agricultural Training Center High School.
- You can consult the training centers and institutes in the Community of Madrid by clicking here .
Agents of the agri-food sector
- Regulatory councils and quality brands of the Community of Madrid .
- Protected Designation of Origin Wines of Madrid .
- Protected Designation of Origin Madrid Oil .
- Protected Geographical Indication Sierra de Guadarrama Meat .
- Geographical Indication of Ávila meat .
- Geographical Denomination Anise of Chinchón.
- Campo Real Olives .
- “M” Certified Product .
- Private sector agents, commercial agents. In addition to the companies included in the "M" certified product category, there is an association of companies in the food and beverage industry in the region called ASEACAM .
- Professional Agricultural Organizations (OPAS). There are four professional organizations: AGIM-COAG , ASAJA-Madrid , the Union of Farmers, Ranchers, and Foresters (UGAMA) , and UPA-Madrid .
- Agricultural Cooperatives, many of them associated with the Union of Agricultural Cooperatives of Madrid (UCAM ).
- Other associations such as the Association of Cattle Farmers for Dairy Control.
Other agents
Local Action Groups (LAGs). Non-profit public-private associations that provide information and process aid related to the sector, as well as promote the rural environment. There are three LAGs in the CM:
- ARACOVE - Aranjuez-Vegas Region Rural Development Association.
- GALSINMA - Sierra Norte de Madrid Local Action Group Association.
- SIERRA OESTE - Association for the Comprehensive Development of the Sierra Oeste of Madrid.
Agricultural Chamber of the CM: It is a consultative and collaborative body with the CM and other Public Administrations and manages the pastures and stubble fields and the Anti-Hail Network of the CM, and provides legal and technical advice to farmers, ranchers and owners of rural properties and to local agricultural associations.
Professional associations: Agricultural Engineers , Agricultural Technicians and Veterinarians .
In addition to these, there are other notable stakeholders linked to advisory services, such as Livestock Health Defense Groups, Integrated Treatment Groups in Agriculture (ATRIAS), and NGOs and consumer organizations that are getting involved in innovative initiatives in the agricultural sector, contributing their experience and channeling consumer interests.
Instruments and tools for the dynamization of the AKIS
REGIONAL STRATEGY FOR SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION
The Community of Madrid has developed two planning instruments in the field of Science, Technology and Innovation: the VI Regional Plan for Scientific Research and Technological Innovation PRICIT 2022-2025 and the Smart and Sustainable Specialization Strategy (S4) .
Both instruments, which are continuations of previous plans, respond to two different regulatory frameworks and have different time frames. However, due to the consistency of objectives and the coincidence of their development over time, the process followed for the development of both instruments has been parallel, taking into account that Smart Specialization encompasses a broad vision of innovation that includes, but is not limited to, technology-driven approaches.
The S4 Strategy, in close collaboration with all stakeholders in the research and innovation system, promotes the effective transfer of knowledge generated in the field of research to the productive sector, with the aim of providing a new boost to productivity, competitiveness, and job creation. The main instrument of this Strategy is the VI Regional Plan for Scientific Research and Technological Innovation (PRCIT) 2022-2025 , which specifies and plans the actions necessary to accelerate these processes. Within the VI PRICIT, Biotechnology and Agrifood is one of the six priority Scientific and Technological Areas, focusing on different fields:
- Fertilizer production, sustainable food for all.
- Applied biotechnology.
- Functional foods and foods for specific applications, such as hospital foods and technologies associated with dysphagia and dysgusia processes.
- Food for the individual: nutraceuticals and nutrigenomics.
- Production of new catalysts and polymers (bioplastics).
There are also other highly relevant tools, such as the Entrepreneurial Discovery Process and the Community of Madrid's programs to promote new industrial activities and support digital transformation.
CAP 2023-2027
Within the scope of the common agricultural policy, the Community of Madrid allocates the following budget and actions to three of the interventions most directly linked to AKIS:
- 7161 (Cooperation of EIP operational groups): €4.82 million.
- 7201 (Training): €0.22 million / Free courses and other training activities in the agricultural, agri-food, forestry, and rural areas.
- 7202 (Advice): €1.17 million.
TOOLS FOR DYNAMIZATION
The Community of Madrid has a Technical Advisory Service for Agricultural Farms, IMIDRA-Madrid Agroasesor , which currently operates in various sectors: livestock, horticulture, woody crops, and field crops, offering farmers and ranchers the results of research generated by IMIDRA.
Networks: Social media and messaging and communication applications have proven to be a very valuable tool for facilitating the flow of knowledge and innovation in the agricultural sector through the creation and development of working groups, meetings, conferences, and congresses. Alongside social media, there are "micronetworks" formed by groups of farmers and ranchers on a temporary and informal basis. This tool is frequently used by advisory services to facilitate peer learning, as is the case with the Professional Agrifood Network (RPA) of the AKIS Advisory Platform.
Additionally, there are institutional networks, such as GENVCE , which specializes in cereals and extensive crops and has a national scope, REMEDIA and the Platform for Extensive Livestock Farming and Pastoralism, and thematic European networks resulting from European projects such as the NEFERTITI project and others promoted by the EIP-AGRI through the H2020 program.
Operational Groups: Within the framework of the Operational Groups (OG) and in charge of the EIP-AGRI, temporary cooperation networks have also been developed with great success in the Autonomous Communities and at the level of trans-autonomous cooperation.
Meeting spaces: A second tool for activating knowledge flows is to promote physical or even virtual meeting spaces. We are referring primarily to meetings, workshops, technical conferences, discussion forums, and conferences, depending on the format and scope.
Publications: At this level, a whole range of opportunities and tools opens up, each with its own dynamics and possibilities. Articles, brochures, posters, monographs, magazines, etc. can be disseminated through digital tools such as Facebook, WhatsApp, YouTube, and Instagram (among others).



